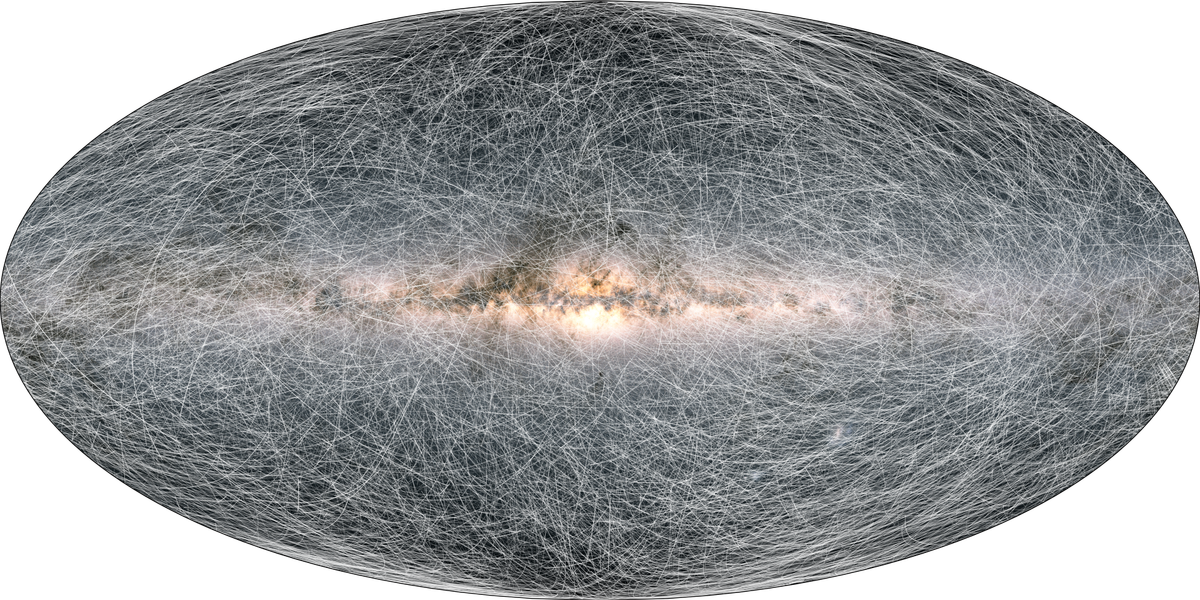
The new map: The latest data pinpoints the location and movements of just under 2 billion stars, with highly accurate measurements of about 300,000 stars within 326 light-years of the solar system. The new map shows us that our solar system’s orbit around the Milky Way is accelerating toward the center of the galaxy by seven millimeters per second.
What could we learn? The point of the mission isn’t simply to get a glimpse of the galaxy’s stars in motion. The data could help astronomers answer a number of different scientific questions, including how the Milky Way was formed over time, where the solar system and other star systems are headed, what the expansion of the universe looks like, and the distribution of regular and dark matter throughout the galaxy. Previous Gaia data sets have been used to ascertain the mass of the Milky Way and how many sun-like stars might be orbited by Earth-light planets.
What’s next: Gaia will be operational until about 2022, but it’s holding up better than expected and could see its mission extend to 2024 or beyond. The final data release should catalogue more than 2 billion objects in the galaxy.



Recent Comments